Instructions for adapting your PD4ML-v3-enabled application to the latest PD4ML API
Category: hint
Creating high quality accessible PDF/UA documents
One of the major reasons to migrate to PD4ML v4 API is the support of the PDF/UA standard (Universal Accessibility).
PDF/UA standard is to let people with disabilities access PDF information in an efficient manner without assistance from others and be able to receive the same value from the content as others. PDF/UA does not add any new features to the PDF file format, but makes some aspects required which are optional in a regular PDF.
A lot of the requirements, like fonts embedding, were implicitly fulfilled even by older versions of PD4ML. But the major ones are covered only starting from PD4ML v4 – thanks to the new product architecture, which has been designed bearing in mind PDF/UA conformance.
PDF/UA requirements
- PDF/UA document must be tagged. It must include information regarding the nesting and relationship of different types of structure elements. It is probably the most annoying task to fulfill if you create PDF/UA using WYSIWYG tools from scratch or do manual PDF post-processing to achieve PDF/UA conformance. With PD4ML the task is trivial: a document structure comes from input HTML and can be perfectly automatically transformed to PDF tags.
- The document structure elements must have alternative descriptions. PD4ML uses for that a content specified by TITLE and ALT attributes of HTML tags. It is also a good idea to specify LANG attribute if the content not in English.
- PDF/UA document must be supplied with XML metadata. PD4ML generates it for you from known document/environment info. Make sure your input HTML document specifies
<title>,<meta name="description" content="document subject">,<meta name="author" content="author name">,<meta name="keywords" content="comma-delimited list of keywords">etc.
Enabling PDF/UA output
First you need to obtain PD4ML UA license with a license code. See the documentation.
Without the license code (or with a code of PD4ML license type, which does not enable PDF/UA feature) it still going to generate PDF/UA documents, but watermarked with “Evaluation” banner.
The next step is straightforward: invoke writePDF() method with PDFUA parameter.
PD4ML pd4ml = new PD4ML();
// important! PDF/UA requires TTF fonts to be embedded
// "arial,times,courier" is a comma-delimited list of font file name patterns to use
pd4ml.useTTF("c:/Windows/Fonts/", "arial,times,courier");
String html = "<html>\n" +
"<head>\n" +
"<title>PDF/UA Test</title>\n" +
"<meta name=\"description\" content=\"Document Subject\" />\n" +
"<meta name=\"author\" content=\"Max Mustermann\" />\n" +
"</head>\n" +
"<body lang=\"DE-de\">\n" +
"<div title=\"PDF/UA test content\">Prüfung auf PDF/UA-Konformität</div>\n" +
"</body>\n" +
"</html>";
ByteArrayInputStream bais =
new ByteArrayInputStream(html.getBytes());
// read and parse HTML
pd4ml.readHTML(bais);
File pdf = File.createTempFile("result", ".pdf");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(pdf);
// render and write the result as PDF
pd4ml.writePDF(fos, Constants.PDFUA);
// open the just-generated PDF with a default PDF viewer
Desktop.getDesktop().open(pdf);
If you run PD4ML as a standalone command line tool, you may force it to output PDF/UA with -outformat pdfua parameter.
In both cases do not forget to point PD4ML to a folder with indexed TTF/OTF fonts using pd4ml.useTTF(fontDir) API call or -ttf <ttf_fonts_dir> command line parameter.
PDF/UA validation
After PDF document is generated, it is a good idea to validate it for PDF/UA conformity. PD4ML did the best, but there are some aspects, that cannot be fully automated (e.g. providing of alternative descriptions).
There is a variety of PDF and PDF/UA validator tools. Our choice is free Free PDF Accessibility Checker (PAC 3)
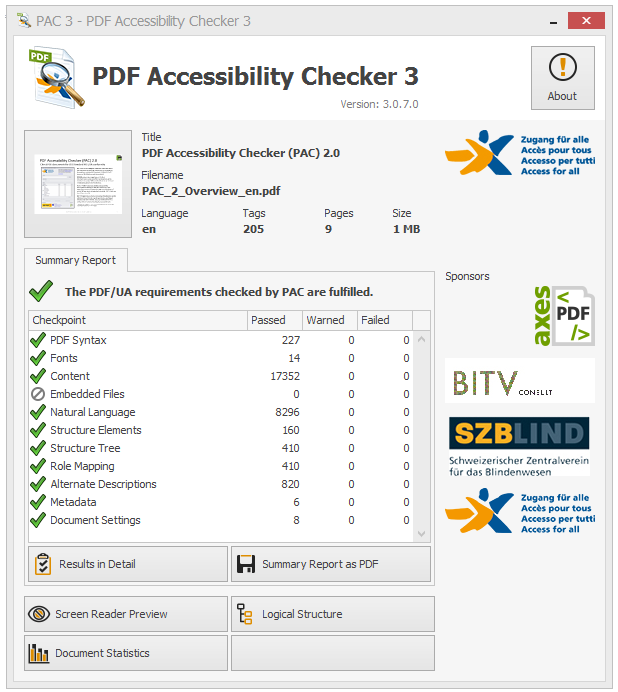
The PAC3 tool creates detailed validation reports, allows to browse the document structure to the problem elements and highlight them in the rendered content. However error messages can be not always clear. With some practice and collected validation experience their meaning becomes less confusing.
Alternatively you may use Preflight included to Adobe Acrobat Pro or diverse online validator applications (e.g. 3-HEIGHTS™ PDF VALIDATOR ONLINE TOOL). The tools are also great, but comparing to PAC3, they are mostly focused not on accessibility issues, but on technical/syntax aspects of PDF code (which should be not your, but our concern).
Most typical validation errors
-
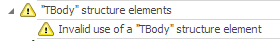 Despite the message, the real validation error reason is a missing of <thead> section in a table. Add missing <thead> section to suppress the message. PD4ML creates an implicit <thead> section if leading table rows contain <th> cells only.
Despite the message, the real validation error reason is a missing of <thead> section in a table. Add missing <thead> section to suppress the message. PD4ML creates an implicit <thead> section if leading table rows contain <th> cells only.
-
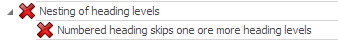 The message is clear: in PDF/UA you are not allowed to nest, let’s say, <h4> heading to <h2>, which happens quite often in real life HTML documents.
The message is clear: in PDF/UA you are not allowed to nest, let’s say, <h4> heading to <h2>, which happens quite often in real life HTML documents.
Creating PDF documents from IBM Notes with PD4ML
v3.x.x v4.1.0
PD4ML can be used to convert IBM Notes documents to PDF (as well as to RTF or to a raster image) a variety of ways.
The most straightforward method is to capture HTML documents, returned by Notes Domino via HTTP: an URL like one of the following is to be passed to render() method of PD4ML.
http://Host/Database/PageUNID?OpenPage
(i.e. http://www.acme.com/discussion.nsf/35AE8FBFA573336A852563D100741784?OpenPage)
http://Host/Database/View/DocumentUniversalID?OpenDocument
(http://www.acme.com/leads.nsf/By+Rep/35AE8FBFA573336A852563D100741784?OpenDocument)
http://Host/Database/FormUniversalID?ReadForm
(http://www.acme.com/products.nsf/625E6111C597A11B852563DD00724CC2?ReadForm)
More IBM Notes URL syntax info…
If you run JSP infrastructure on IBM Domino server, another online method of PDF generation would be to use PD4ML JSP custom tag library (TODO).
If an online document generation method (involving HTTP, JSP etc) is undesired, there is a possibility to generate PDF documents from their XML representations (so called DXL).
DXL is an adaptation of XML used to describe, in detail, the structure and data contained in a Domino database. It describes data and design elements such as views, forms, and documents and provides a basis for importing or exporting XML representations of data to and from a Domino/Notes application.
Schematically a process of Notes document conversion to PDF can be seen like that:
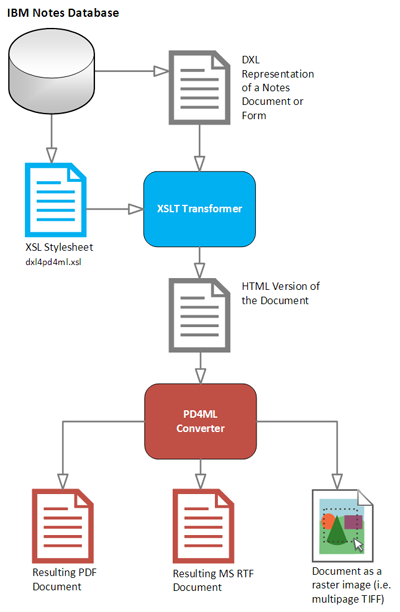
All conversion steps can be implemented at once as a IBM Lotus Notes Java agent, or can be implemented as two-step batch: DXL export request followed by a conversion with Pd4Cmd command-line tool
java -Djava.awt.headless=true -Xmx512m -jar pd4ml.jar test.dxl 1200 -xsl notesdefault
The command line overrides the default Java memory heap size limit with -Xmx512m. Here it is set to 512Mb.
On UNIX platform -Djava.awt.headless=true allows to run the application on non-graphics-enabled servers or from remote ssh/telnet sessions.
test.dxl 1200 are DXL location and htmlWidth (virtual “browser” frame width) parameters.
On Win32 the path is enclosed, if needed, to double quotes, on UNIX – to single quotes.
-xsl notesdefault applies XSL stylesheet to the input document. In the case it refers to the built-in default DXL-to-HTML XSL, but it can be an URI of an arbitrary external stylesheet.
The default PDF document format: A4 / PORTRAIT
In the example 1200px width of rendered document will be mapped to 595pt widths of A4 page format.
As long as an output file path omitted, the output is sent to STDOUTand can be piped to another application.
See more command line arguments…
PD4ML as Notes Agent…
PD4ML Integration with Macromedia® ColdFusion®
Please follow the link to the corresponding section in the Reference manual.
2. Integration of PD4ML with ColdFusion Standard edition
Unfortunately not all runtime modes of ColdFusion allow to use JSP tag libraries. In that case the only way to
integrate PD4ML is to use PD4ML Java API.
The following is the integration example .cfm contributed by David REYNAUD:
<html>
<head>
<title>PD4ML under CFMX 6.x Std Edition</title>
</head>
<body>
<!---
BEFORE RUNNING :
Idea 1 :
put the JAR file : pd4ml_demo.jar
in the same folder as current CFM page
Idea 2 :
maybe you can put the JAR file : pd4ml_demo.jar
into the ColfdFusion's CustomTags directory
Idea 3 :
use the ColdFusion Admin to configure classpath to use the jar
--->
<cfscript>
// The source file to convert (http:// or file:)
inURI="file:n:/web/tests/pd4ml/test.html";
// The pdf file to generate (full pathname)
fileOut="n:/web/tests/pd4ml/test.pdf";
unnitsvalue="mm"; // Millimeters
// A4 'vertical' in mm
format = createObject("java","java.awt.Dimension").init(210,297);
topValue = 10; // mm
leftValue = 10; // mm
rightValue = 10; // mm
bottomValue = 10; // mm
landscapevalue="yes";
userSpaceWidth=780; // px
splitValue=0;
patchValue=1;
authorName="";
// PD4ML Object instantiation
pd4ml = createObject("java","org.zefer.pd4ml.PD4ML");
// Format, orientation, insets
if (landscapeValue) format = pd4ml.changePageOrientation(format);
insets = createObject("java","java.awt.Insets")
.init(topValue,leftValue,bottomValue,rightValue);
if (unnitsvalue EQ "mm") {
pd4ml.setPageSizeMM(format);
pd4ml.setPageInsetsMM(insets);
} else {
pd4ml.setPageSize(format);
pd4ml.setPageInsets(insets);
}
if(authorName NEQ "")
pd4ml.setAuthorName(authorname);
if (userSpaceWidth NEQ "") pd4ml.setHtmlWidth( userSpaceWidth );
pd4ml.enableImgSplit( splitValue );
pd4ml.enableRenderingPatch( patchValue );
fos = createObject("java","java.io.FileOutputStream").init(fileOut);
pd4ml.render(inURI,fos); // Start rendering
</cfscript>
<cfoutput>File '#inURI#' converted to '#fileOut#'</cfoutput>
</body>
</html>
.NET port of PD4ML
PD4ML.NET is a 100% managed code port of PD4ML v3 conversion library, which allows you to create Adobe PDF documents on the fly from HTML documents or templates.
- Built-in security by using code access security and avoiding buffer overruns, which is very critical for server-side applications.
- Performance benefits gained from executing all code in the Common Language Runtime with use of the Just-In-Time compiler. Calling unmanaged code decreases performance because additional security checks are required.
- Ease of deployment
- Improved versioning.
- Implicit lifetime control of objects and garbage collection.
PD4ML.NET is encapsulated in an easy-to-deploy set of DLLs and it does not rely on any unsafe native components (like MS Internet Explorer renderer): it is based on proprietary HTML rendering engine, optimized for PDF layout generation. The rendering engine implements most of HTML4/CSS2 standard features plus a number of custom PDF-generation-specific functions: pagination control, headers/footers generation, watermarking, TOC generation etc.
PDF reporting does not require an utilization of complex report generators anymore. You create an HTML/ASP based report with images, charts, form elements and PD4ML.NET does the rest for you.
The component can be used from any .NET 1.1/2.0/3.x application (Windows forms, ASP.NET Web sites or command line tools), even if the application run under Mono framework on Linux platform.
Main features:
- Convert an URL or HTML string to a PDF file or byte stream.
- Set PDF page format and orientation
- Control page margins
- Define PDF headers and footers in HTML (including images and page numbers)
- Embed and use True Type and Open Type fonts.
- Support most of Asian, Middle-East, European and Latin character sets
- Generate external and internal hyperlinks
- Control header/footer appearance on selected pages
- Embed attachments
- Switch PDF encryption on and assign document security restrictions
- Generate PDF bookmarks
- Generate table of contents based on <H1>-<H6> structure
- Customize page background
- Watermark pages
- Override hardcoded document style with additional CSS style sheets
- Provide basic support for PDF forms
The rich set of features and the robustness of the managed code makes PD4ML famous as a perfect PDF generation solution for server-side and desktop applications.
Additional info:
How to configure PDF fonts
PD4ML PRO, DMS and UA allow you to use all UNICODE characters space of custom TTF/OTF fonts in PDF.
The way TTF embedding is implemented by PD4ML may look complicated at first glance. On practice it is not so; also there are reasons why TTF usage is not as transparent as in regular Java applications.
In Java you can easily instantiate java.awt.Font object for any font face name, obtain the font metrics and to set the font for text output. By PDF generation PD4ML needs an access not only to java.awt.Font object, but to the corresponding physical .ttf file (to parse them and to extract a subset of used glyphs). Unfortunately Java does not offer a way to locate TTF file for a particular java.awt.Font object.
The most straightforward solution was to use font face -> font file mapping file. PD4ML’s default file name for it is pd4fonts.properties
New since v4.0.16: Interactive pd4fonts.properties creation tool: https://pd4ml.com/pd4ml-fonts-tool/
Below are available options how to create and deal with the mapping file or how to avoid a creation of it.
Creation of pd4fonts.properties for a selected set of fonts
- create fonts/ directory (i.e /path/to/my/fonts/) and copy desired TTF files into it.
- run pd4fonts.properties generation command
java -Xmx512m -jar pd4ml.jar -configure.fonts /path/to/my/fonts/
As a result it should produce /path/to/my/fonts/pd4fonts.properties.
Now you can refer to it from Java application
pd4ml.useTTF("/path/to/my/fonts/");
// or identically
pd4ml.useTTF("/path/to/my/fonts/pd4fonts.properties");
Creation of pd4fonts.properties for system fonts
In the example above pd4fonts.properties file is stored to the same folder where TTF files are. If you run the command to index system fonts, in most of the cases it fails, as it has no write permission to the system font folder.
A solution is to write pd4fonts.properties to another location:
- run pd4fonts.properties generation command
java -Xmx512m -jar pd4ml.jar -configure.fonts c:/windows/fonts/ c:/path/to/my/config
As a result it should produce c:/path/to/my/config/pd4fonts.properties with an internal reference to the original font folder c:/windows/fonts/.
Now you may refer to it from Java application
pd4ml.useTTF("c:/path/to/my/config");
// or identically
pd4ml.useTTF("c:/path/to/my/config/pd4fonts.properties");
Creation of pd4fonts.properties on-a-fly
Set generateFontMappingFileIfMissing parameter of useTTF() to true
pd4ml.useTTF("/path/to/my/fonts/", true);
Creation of in-memory font mapping on-a-fly
Typically the method is used, when there is no preconfigured fonts directory available, and a use of the system fonts directory seems to be a good option. An obvious drawback of the idea is a potentially long indexing time of a big number of system fonts.
PD4ML allows to reduce the indexing efforts by limiting a scope of used fonts. fontFileNameFilter parameter can be set to a comma-delimited list of font name patterns:
pd4ml.useTTF("c:/windows/fonts/", "arial,times,courier");
The above code forces PD4ML to index only fonts, whose names contain arial, times or courier.
Creation of a JAR file with fonts
As a rule in Web application contexts you are not allowed to refer local file system resources. That makes the above methods not usable. PD4ML’s solution is to pack the fonts to a JAR file and deploy it with the Web application resources.
- create fonts/ directory (i.e /path/to/my/fonts/) and copy desired TTF files into it.
- run pd4fonts.properties generation command
java -Xmx512m -jar pd4ml.jar -configure.fonts /path/to/my/fonts/
which produces /path/to/my/fonts/pd4fonts.properties
- pack to JAR
jar cvf fonts.jar /path/to/my/fonts/
After deployment you can refer to it from Java application
pd4ml.useTTF("java:fonts/");
The “java:fonts/” URL addresses fonts/ folder within the JAR.
Web fonts
The @font-face CSS at-rule adds a custom font to a list of available ones; the font can be loaded from either a remote server or a locally-installed font on the user’s own computer.
The approach requires no API calls. All configuration is to be done in HTML/CSS sources.
@font-face {
font-family: "Consolas";
src: url("java:/html/rc/FiraMono-Regular.ttf") format("ttf");
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'Open Sans';
font-style: normal;
font-weight: 400;
src: url(https://fonts.gstatic.com/s/lato/v11/qIIYRU-oROkIk8vfvxw6QvesZW2xOQ-xsNqO47m55DA.woff) format('woff');
}
Font kerning
Kerning is an addition or reduction of space between two characters (glyphs) of a proportional font. As a rule a rendered text is visually much more pleasing when the kerning is applied.
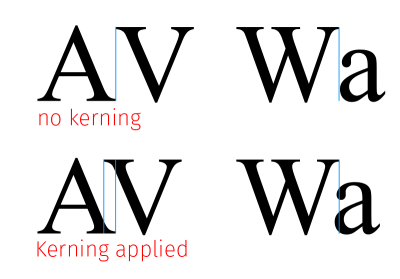
Font kerning can be enabled with PD4ML API call:
pd4ml.applyKerning(true);
If you run PD4ML as a standalone command line tool, you may force it to apply kerning with -kerning parameter.


